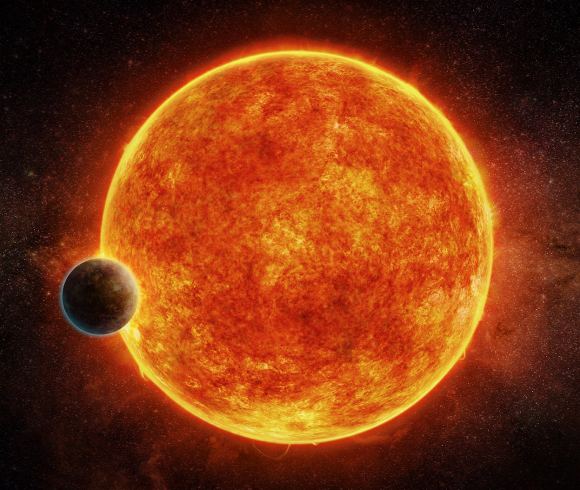
A Total Solar Eclipse of Saros 145:
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2017 August 11
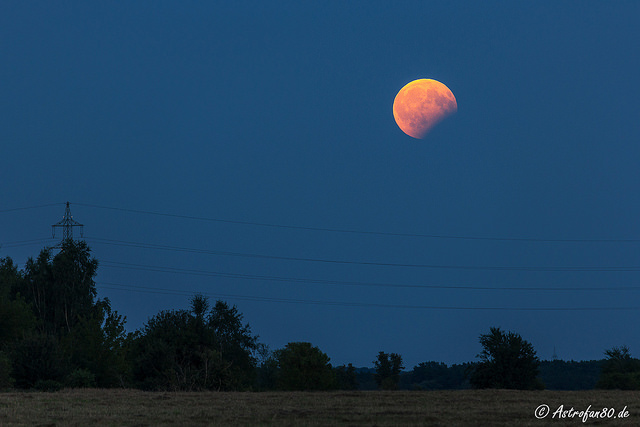
A Total Solar Eclipse of Saros 145
Image Credit & Copyright: Tunç Tezel (TWAN), Alkim Ün
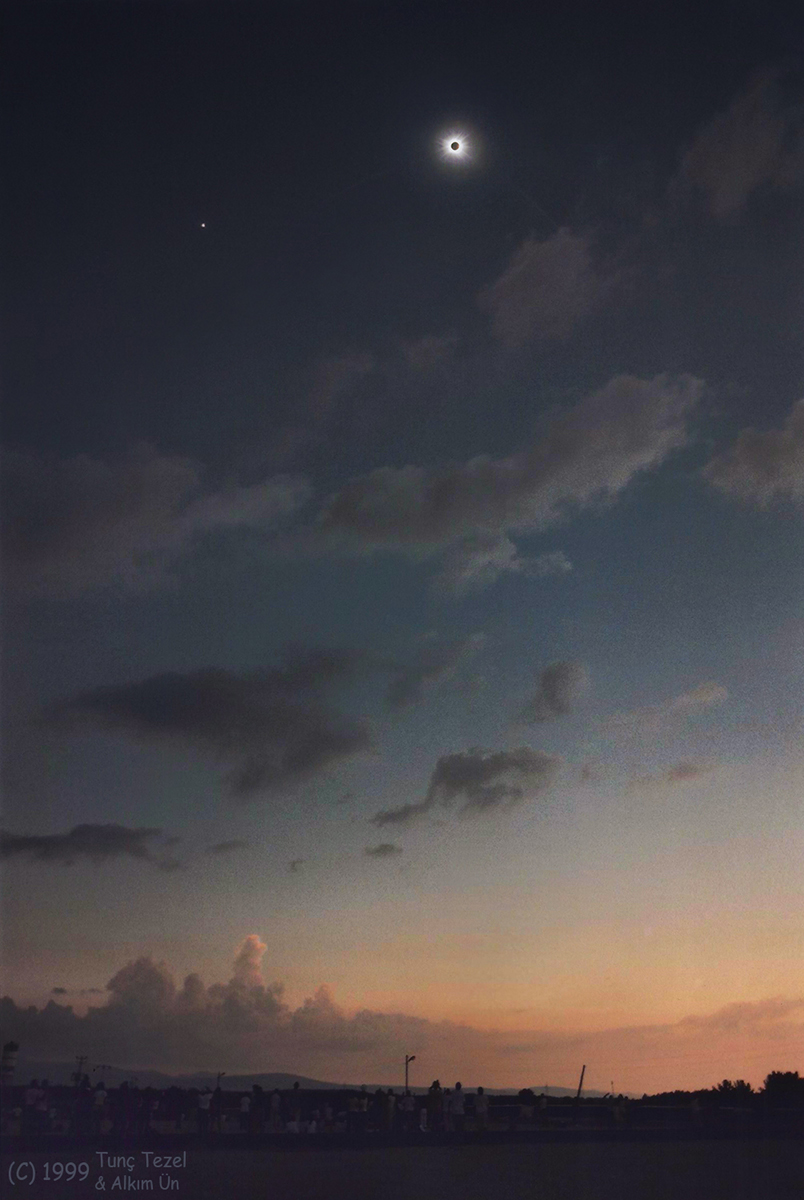
Explanation: A darkened sky holds bright planet Venus, the New Moon in silhouette, and the shimmering corona of the Sun in this image of a total solar eclipse. A composite of simultaneous telephoto and wide angle frames it was taken in the path of totality 18 years ago, August 11, 1999, near Kastamonu, Turkey. That particular solar eclipse is a member of Saros 145. Known historically from observations of the Moon's orbit, the Saros cycle predicts when the Sun, Earth, and Moon will return to the same geometry for a solar (or lunar) eclipse. The Saros has a period of 18 years, 11 and 1/3 days. Eclipses separated by one Saros period belong to the same numbered Saros series and are very similar. But the path of totality for consecutive solar eclipses in the same Saros shifts across the Earth because the planet rotates for an additional 8 hours during the cycle's fractional day. So the next solar eclipse of Saros 145 will also be a total eclipse, and the narrow path of totality will track coast to coast across the United States on August 21, 2017.
Tomorrow's picture: day of the gnomons
< | Archive | Submissions | Index | Search | Calendar | RSS | Education | About APOD | Discuss | >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Photos of Nature, Nature Photography Across The Universe. All about Nature, Love, Travel, Beautiful Photo, Landscape, Sunset, Summer, Mountains, Flowers, Photographer, Wallpaper, Portrait, Photo, what is the Universe
Photos of Nature | Nature Photography What is The Universe
Wednesday, August 16, 2017
Detailed View of a Solar Eclipse Corona
Detailed View of a Solar Eclipse Corona:
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2017 August 13
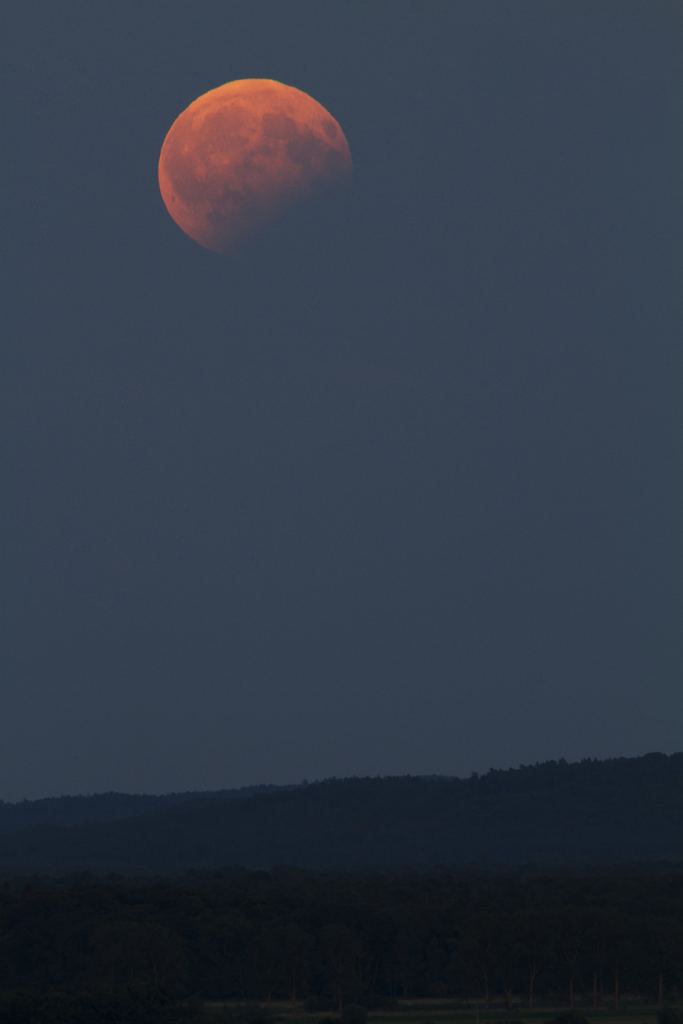
Detailed View of a Solar Eclipse Corona
Image Credit & Copyright: Miloslav Druckmüller (Brno U. of Tech.), Martin Dietzel, Peter Aniol, Vojtech Rušin
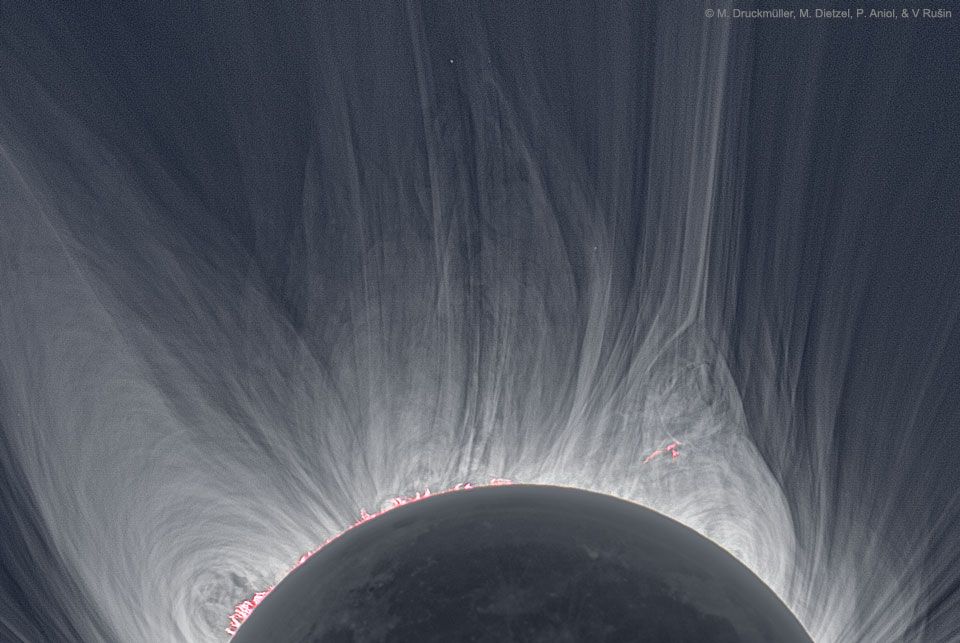
Explanation: Only in the fleeting darkness of a total solar eclipse is the light of the solar corona easily visible. Normally overwhelmed by the bright solar disk, the expansive corona, the sun's outer atmosphere, is an alluring sight. But the subtle details and extreme ranges in the corona's brightness, although discernible to the eye, are notoriously difficult to photograph. Pictured here, however, using multiple images and digital processing, is a detailed image of the Sun's corona taken during the 2008 August total solar eclipse from Mongolia. Clearly visible are intricate layers and glowing caustics of an ever changing mixture of hot gas and magnetic fields. Bright looping prominences appear pink just above the Sun's limb. A similar solar corona might be visible through clear skies in a thin swath across the USA during a total solar eclipse that occurs just one week from tomorrow.
Citizen Science: How to participate during the Aug. 21 eclipse.
Tomorrow's picture: New Horizons over Charon
< | Archive | Submissions | Index | Search | Calendar | RSS | Education | About APOD | Discuss | >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2017 August 13
Detailed View of a Solar Eclipse Corona
Image Credit & Copyright: Miloslav Druckmüller (Brno U. of Tech.), Martin Dietzel, Peter Aniol, Vojtech Rušin
Explanation: Only in the fleeting darkness of a total solar eclipse is the light of the solar corona easily visible. Normally overwhelmed by the bright solar disk, the expansive corona, the sun's outer atmosphere, is an alluring sight. But the subtle details and extreme ranges in the corona's brightness, although discernible to the eye, are notoriously difficult to photograph. Pictured here, however, using multiple images and digital processing, is a detailed image of the Sun's corona taken during the 2008 August total solar eclipse from Mongolia. Clearly visible are intricate layers and glowing caustics of an ever changing mixture of hot gas and magnetic fields. Bright looping prominences appear pink just above the Sun's limb. A similar solar corona might be visible through clear skies in a thin swath across the USA during a total solar eclipse that occurs just one week from tomorrow.
Citizen Science: How to participate during the Aug. 21 eclipse.
Tomorrow's picture: New Horizons over Charon
< | Archive | Submissions | Index | Search | Calendar | RSS | Education | About APOD | Discuss | >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Charon Flyover from New Horizons
Charon Flyover from New Horizons:
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2017 August 14
Charon Flyover from New Horizons
Video Credit: NASA, JHUAPL, SwRI, P. Schenk & J. Blackwell (LPI); Music: Juicy by ALBIS
Explanation: What if you could fly over Pluto's moon Charon -- what might you see? The New Horizons spacecraft did just this in 2015 July as it zipped past Pluto and Charon with cameras blazing. The images recorded allowed for a digital reconstruction of much of Charon's surface, further enabling the creation of fictitious flights over Charon created from this data. One such fanciful, minute-long, time-lapse video is shown here with vertical heights and colors of surface features digitally enhanced. Your journey begins over a wide chasm that divides different types of Charon's landscapes, a chasm that might have formed when Charon froze through. You soon turn north and fly over a colorful depression dubbed Mordor that, one hypothesis holds, is an unusual remnant from an ancient impact. Your voyage continues over an alien landscape rich with never-before-seen craters, mountains, and crevices. The robotic New Horizons spacecraft has now been targeted at Kuiper Belt object 2014 MU 69, which it should zoom past on New Year's Day 2019.
Tomorrow's picture: stars versus stardust
< | Archive | Submissions | Index | Search | Calendar | RSS | Education | About APOD | Discuss | >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2017 August 14
Charon Flyover from New Horizons
Video Credit: NASA, JHUAPL, SwRI, P. Schenk & J. Blackwell (LPI); Music: Juicy by ALBIS
Explanation: What if you could fly over Pluto's moon Charon -- what might you see? The New Horizons spacecraft did just this in 2015 July as it zipped past Pluto and Charon with cameras blazing. The images recorded allowed for a digital reconstruction of much of Charon's surface, further enabling the creation of fictitious flights over Charon created from this data. One such fanciful, minute-long, time-lapse video is shown here with vertical heights and colors of surface features digitally enhanced. Your journey begins over a wide chasm that divides different types of Charon's landscapes, a chasm that might have formed when Charon froze through. You soon turn north and fly over a colorful depression dubbed Mordor that, one hypothesis holds, is an unusual remnant from an ancient impact. Your voyage continues over an alien landscape rich with never-before-seen craters, mountains, and crevices. The robotic New Horizons spacecraft has now been targeted at Kuiper Belt object 2014 MU 69, which it should zoom past on New Year's Day 2019.
Tomorrow's picture: stars versus stardust
< | Archive | Submissions | Index | Search | Calendar | RSS | Education | About APOD | Discuss | >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Stars, Gas, and Dust Battle in the Carina Nebula
Stars, Gas, and Dust Battle in the Carina Nebula:
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2017 August 15
Stars, Gas, and Dust Battle in the Carina Nebula
Image Credit & Copyright: Bastien Foucher
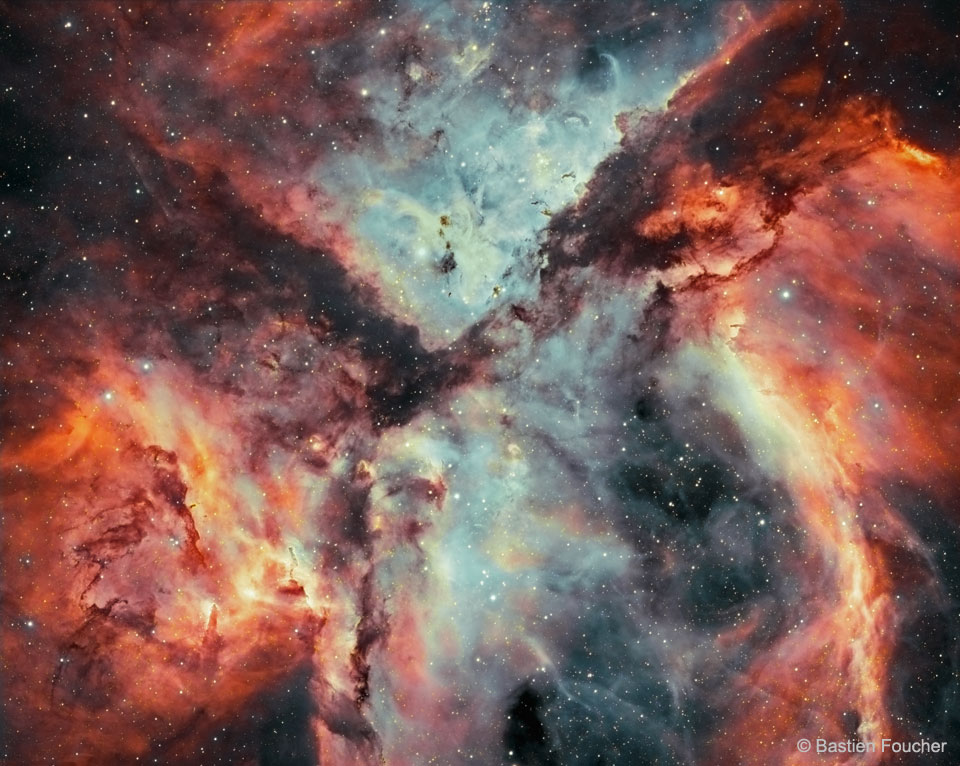
Explanation: Chaos reigns in the Carina Nebula where massive stars form and die. Striking and detailed, this close-up of a portion of the famous nebula is a combination of light emitted by hydrogen (shown in red) and oxygen (shown in blue). Dramatic dark dust knots and complex features revealed are sculpted by the winds and radiation of Carina's massive and energetic stars. One iconic feature of the Carina Nebula is the dark V-shaped dust lane that occurs in the top half of the image. The Carina Nebula spans about 200 light years, lies about 7,500 light years distant, and is visible with binoculars toward the southern constellation of Carina. In a billion years after the dust settles -- or is destroyed, and the gas dissipates -- or gravitationally condenses, then only the stars will remain -- but not even the brightest ones.
Tomorrow's picture: interplanetary dust
< | Archive | Submissions | Index | Search | Calendar | RSS | Education | About APOD | Discuss | >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2017 August 15
Stars, Gas, and Dust Battle in the Carina Nebula
Image Credit & Copyright: Bastien Foucher
Explanation: Chaos reigns in the Carina Nebula where massive stars form and die. Striking and detailed, this close-up of a portion of the famous nebula is a combination of light emitted by hydrogen (shown in red) and oxygen (shown in blue). Dramatic dark dust knots and complex features revealed are sculpted by the winds and radiation of Carina's massive and energetic stars. One iconic feature of the Carina Nebula is the dark V-shaped dust lane that occurs in the top half of the image. The Carina Nebula spans about 200 light years, lies about 7,500 light years distant, and is visible with binoculars toward the southern constellation of Carina. In a billion years after the dust settles -- or is destroyed, and the gas dissipates -- or gravitationally condenses, then only the stars will remain -- but not even the brightest ones.
Tomorrow's picture: interplanetary dust
< | Archive | Submissions | Index | Search | Calendar | RSS | Education | About APOD | Discuss | >
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Prometheus and the Ghostly F Ring
Prometheus and the Ghostly F Ring: The thin sliver of Saturn's moon Prometheus lurks near ghostly structures in Saturn's narrow F ring in this view from NASA's Cassini spacecraft.
| Original enclosures: |
Moon Rise From the Space Station
Moon Rise From the Space Station: From his vantage point aboard the International Space Station, NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik pointed his camera toward the rising Moon and captured this beautiful image on August 3, 2017. Bresnik wrote, "Gorgeous moon rise! Such great detail when seen from space. Next full moon marks #Eclipse2017. We’ll be watching from @Space_Station."
| Original enclosures: |
A Starburst with the Prospect of Gravitational Waves
A Starburst with the Prospect of Gravitational Waves: More than a hundred years after Swift’s discovery of the "starburst" galaxy IC 10, astronomers are studying IC 10 with the most powerful telescopes of the 21st century.
| Original enclosures: |
Hubble Displays a Dwarf Spiral Galaxy
Hubble Displays a Dwarf Spiral Galaxy: Dwarf galaxy NGC 5949 sits at a distance of around 44 million light-years from us, placing it within the Milky Way’s cosmic neighborhood.
| Original enclosures: |
Highlighting Titan's Hazes
Highlighting Titan's Hazes: NASA's Cassini spacecraft looks toward the night side of Saturn's moon Titan in a view that highlights the extended, hazy nature of the moon's atmosphere.
| Original enclosures: |
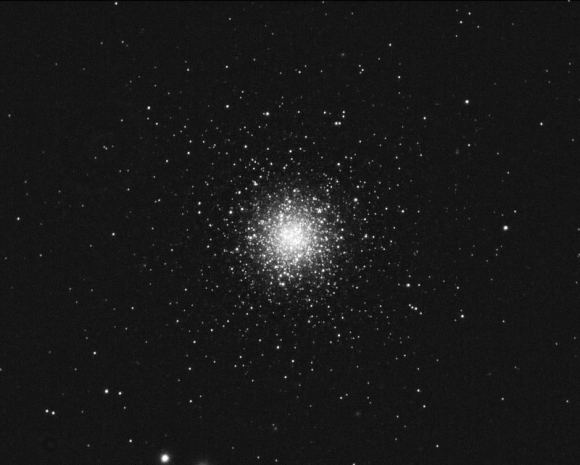
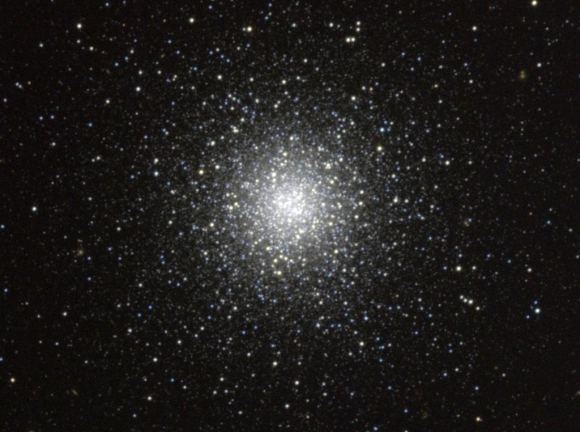
Messier 53 – the NGC 5024 Globular Cluster
Messier 53 – the NGC 5024 Globular Cluster:
Welcome back to Messier Monday! In our ongoing tribute to the great Tammy Plotner, we take a look at globular cluster known as Messier 53!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noted the presence of several “nebulous objects” in the night sky. Having originally mistaken them for comets, he began compiling a list of these objects so others would not make the same mistake he did. In time, this list (known as the Messier Catalog) would come to include 100 of the most fabulous objects in the night sky.
One of these objects is Messier 53, a globular cluster located in the northern Coma Berenices constellation. Located about 58,000 light years from the Solar System, it is almost equidistant from Galactic Center (about 60,000 light years). As Messier Objects go, it is relatively easy to find since it lies in the same area of the sky as Arcturus, the fourth brightest star in the night sky.
According to G. Beccari (et al) the population of these definitely appears to violate standard theories of stellar evolution. And there not just a few blues… There’s a whole host of them. As Beccari noted in a 2008 study:
He would return again in later years to include in his notes: “From what has been said it is obvious that here the exertion of a clustering power has brought the accumulation and artificial construction of these wonderful celestial objects to the highest degree of mysterious perfection.”
Although it did not touch Sir John Herschel quite so much, M53 also engaged Admiral Smyth who wrote:
To see this small globular cluster in binoculars will require dark skies and it will appear very small, like a large, out of focus star. In small telescopes it will appear almost cometary – and thus why Messier cataloged these objects! However, with telescopes approaching the 6″ range, resolution will begin and larger telescopes will shatter this gorgeous globular cluster. Requires dark skies.
The location of Messier 53 in the northern Coma Berenices constellation. Credit: IAU and Sky & Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg)A ball of worlds… What a unique description! May you enjoy your observations as well!
And here are the quick facts on this Messier Object to help you get started!
Object Name: Messier 53
Alternative Designations: M53, NGC 5024
Object Type: Class V Globular Cluster
Constellation: Coma Berenices
Right Ascension: 13 : 12.9 (h:m)
Declination: +18 : 10 (deg:m)
Distance: 58.0 (kly)
Visual Brightness: 7.6 (mag)
Apparent Dimension: 13.0 (arc min)
We have written many interesting articles about Messier Objects here at Universe Today. Here’s Tammy Plotner’s Introduction to the Messier Objects, , M1 – The Crab Nebula, M8 – The Lagoon Nebula, and David Dickison’s articles on the 2013 and 2014 Messier Marathons.
Be to sure to check out our complete Messier Catalog. And for more information, check out the SEDS Messier Database.
Sources:
The post Messier 53 – the NGC 5024 Globular Cluster appeared first on Universe Today.
Welcome back to Messier Monday! In our ongoing tribute to the great Tammy Plotner, we take a look at globular cluster known as Messier 53!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noted the presence of several “nebulous objects” in the night sky. Having originally mistaken them for comets, he began compiling a list of these objects so others would not make the same mistake he did. In time, this list (known as the Messier Catalog) would come to include 100 of the most fabulous objects in the night sky.
One of these objects is Messier 53, a globular cluster located in the northern Coma Berenices constellation. Located about 58,000 light years from the Solar System, it is almost equidistant from Galactic Center (about 60,000 light years). As Messier Objects go, it is relatively easy to find since it lies in the same area of the sky as Arcturus, the fourth brightest star in the night sky.
Description:
Heading towards us at a speed of 112 kilometers per second, globular cluster M53 is one of the furthest distant globular clusters in our Milky Way halo and lay almost equally distant between our solar system and the galactic center. This 220 light year diameter ball of stars in tightly compacted towards its core – where low metal is the name of the game and RR Lyra type variable stars once ruled. But recent studies have found that there are some new kids on the block. The blue stragglers…According to G. Beccari (et al) the population of these definitely appears to violate standard theories of stellar evolution. And there not just a few blues… There’s a whole host of them. As Beccari noted in a 2008 study:
“We used a proper combination of high-resolution and wide-field multiwavelength observations collected at three different telescopes (HST, LBT, and CFHT) to probe the blue straggler star (BSS) population in the globular cluster M53. Almost 200 BSSs have been identified over the entire cluster extension. We have also used this database to construct the radial star density profile of the cluster; this is the most extended and accurate radial profile ever published for this cluster, including detailed star counts in the very inner region. A deviation from the model is noted in the most external region of the cluster. This feature needs to be further investigated in order to address the possible presence of a tidal tail in this cluster.”Is this possible? Then take a closer look into this research. One where a millisecond pulsar was discovered inside. As S.R. Kulkarni (et al) indicated in a 1991 study:
“Millisecond pulsars are conventionally assumed to be spun up through the action of binary companions, although some subsequently lose their companions and appear as isolated pulsars. Such objects should therefore be more numerous in dense stellar systems. We report here the surprising discovery of two pulsars in low-density globular clusters: one is a single 10-ms pulsar (1639+36) in M13 (NGC 6205), the other a 33-ms pulsar (1310+18) in a 256-d binary in M53 (NGC 5024). Their ages, inferred from their luminosities and constraints on their period derivatives, seem to be 10 9 years, significantly greater than previously reported ages ( ! 10 8 years) of cluster pulsars. The implied birth rate is inconsistent with the conventional two-body tidal capture model, suggesting that an alternative mechanism such as tidal capture between primordial binaries and a reservoir of (hundreds of) primordial neutron stars may dominate the production of tidal binaries in such clusters. The period derivative of PSR1639+36 is surprisingly small, and may be corrupted by acceleration due to the mean gravitational potential of the cluster.”
History of Observation:
This globular cluster was first discovered on February 3, 1775 by Johann Elert Bode, but independently recovered on February 26, 1777 by Charles Messier who writes:“Nebula without stars discovered below & near Coma Berenices, a little distant from the star 42 in that constellation, according to Flamsteed. This nebula is round and conspicuous. The Comet of 1779 was compared directly with this nebula, & M. Messier has reported it on the chart of that comet, which will be included in the volume of the Academy for 1779. Observed again April 13, 1781: It resembles the nebula which is below Lepus [M79].”Sir William Herschel would revisit M53, but he did not publish his findings when studying Messier objects. Very seldom did Herschel wax poetic in his writings, but of this particular object he said: “A cluster of very close stars; one of the most beautiful objects I remember to have seen in the heavens. The cluster appears under the form of a solid ball, consisting of small stars, quite compressed into one blaze of light, with a great number of loose ones surrounding it, and distinctly visible in the general mass.”
He would return again in later years to include in his notes: “From what has been said it is obvious that here the exertion of a clustering power has brought the accumulation and artificial construction of these wonderful celestial objects to the highest degree of mysterious perfection.”
Although it did not touch Sir John Herschel quite so much, M53 also engaged Admiral Smyth who wrote:
“A globular cluster, between Berenice’s tresses and the Virgin’s left hand, with a coarse pair of telescopic stars in the sf [south following, SE] quadrant, and a single one in the sp [south preceding, SW]. This is a brilliant mass of minute stars, from the 11th to the 15th magnitude, and from thence to gleams of star-dust, with stragglers to the np [north preceding, NW], and pretty diffused edges. From the blaze at the centre, it is evidently a highly compressed ball of stars, whose law of aggregation into so dense and compact a mass, is utterly hidden from our imperfect senses. It was enrolled by Messier in 1774 as No. 53, and resolved into stars by Sir W. Herschel. The contemplation of so beautiful an object, cannot but set imagination to work, though the mind may be soon lost in astonishment at the stellar dispositions of the great Creator and Maintainer. Thus, in reasoning by analogy, these compressed globes of stars confound conjecture as to the models in which the mutual attractions are prevented from causing the universal destruction of their system. Sir John Herschel thinks, that no pressure can be propagated through a cluster of discrete stars; whence it would follow, that the permanence of its form must be maintained in a way totally different from that which our reasoning suggest. Before quitting this interesting ball of innumerable worlds, I may mention that it was examined by Sir John Herschel, with Mr. Baily, in the 20-foot reflector; and that powerful instrument showed the cluster with curved appendages of stars, like the short claws of a crab running out from the main body. A line through Delta and Epsilon Virginis, northward, meeting another drawn from Arcturus to Eta Bootis, unite upon this wonderful assemblage; or it is also easily found by its being about 1 deg northeast of 42 Comae Berenices, the alignment of which is already given.”
Locating Messier 53:
M53 can be easily found just about a degree northeast of 42 Alpha Comae Berenices, a visual binary star. To located Alpha, draw a mental line from Arcturus via Eta Bootis where you’ll see it about a fist width west. Alternately you can starhop from Gamma Viginis to Delta and on to Epsilon where you can locate M53 approximately 4 fingerwidths to the north/northeast.To see this small globular cluster in binoculars will require dark skies and it will appear very small, like a large, out of focus star. In small telescopes it will appear almost cometary – and thus why Messier cataloged these objects! However, with telescopes approaching the 6″ range, resolution will begin and larger telescopes will shatter this gorgeous globular cluster. Requires dark skies.
The location of Messier 53 in the northern Coma Berenices constellation. Credit: IAU and Sky & Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg)
And here are the quick facts on this Messier Object to help you get started!
Object Name: Messier 53
Alternative Designations: M53, NGC 5024
Object Type: Class V Globular Cluster
Constellation: Coma Berenices
Right Ascension: 13 : 12.9 (h:m)
Declination: +18 : 10 (deg:m)
Distance: 58.0 (kly)
Visual Brightness: 7.6 (mag)
Apparent Dimension: 13.0 (arc min)
We have written many interesting articles about Messier Objects here at Universe Today. Here’s Tammy Plotner’s Introduction to the Messier Objects, , M1 – The Crab Nebula, M8 – The Lagoon Nebula, and David Dickison’s articles on the 2013 and 2014 Messier Marathons.
Be to sure to check out our complete Messier Catalog. And for more information, check out the SEDS Messier Database.
Sources:
The post Messier 53 – the NGC 5024 Globular Cluster appeared first on Universe Today.
Gorgeous Images of the August 2017 Partial Lunar Eclipse
Gorgeous Images of the August 2017 Partial Lunar Eclipse:
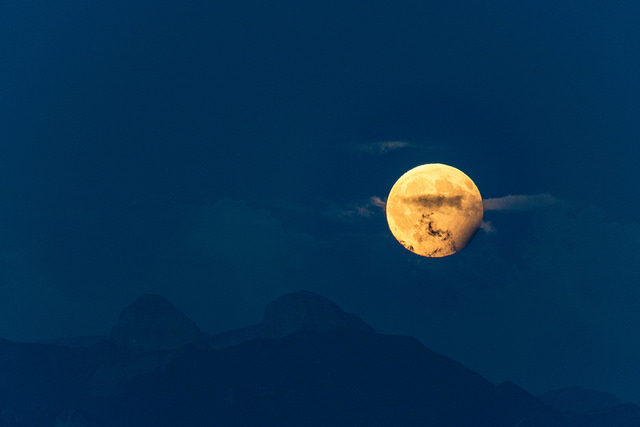
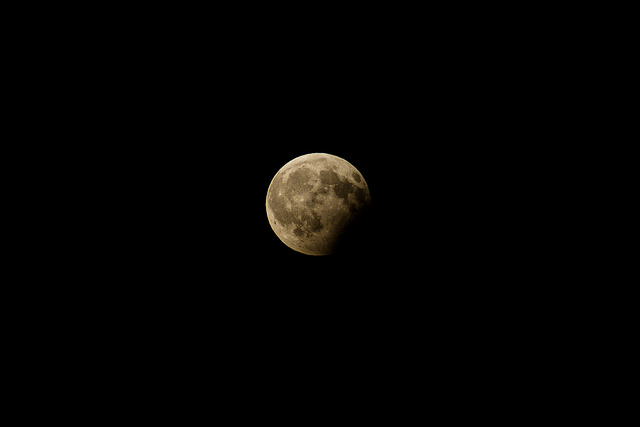
Just to get you in the mood for the upcoming total solar eclipse — now less than two weeks away — our Solar System put on a little eclipse display of the lunar kind on August 7. The full Moon passed through part of the Earth’s umbral shadow, and the timing made this partial lunar eclipse visible in parts of Europe and Africa.
Thanks to our friends around the world who posted in Universe Today’s Flickr page, we’ve got images to share! Enjoy the views! Click on all the images to see larger versions of them on Flickr. The lead image link is here.
And for those of you in the path of the August 21 solar eclipse, please feel free to share your images on our Flickr page, and we may feature them in an upcoming article.
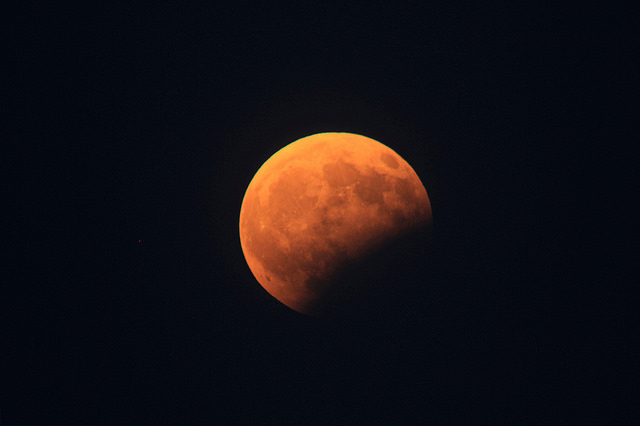
A composite of images take during the August 2017 lunar eclipse, as see from Kuala Lumpur. Credit and copyright: Shahrin Ahmad.
Partial lunar eclipse seen from Lausanne’s lakeshore in Switzerland … The Moon had just moved up from behind the Tour d’Aï Peaks. Credit and copyright: Hicham Dennaoui.
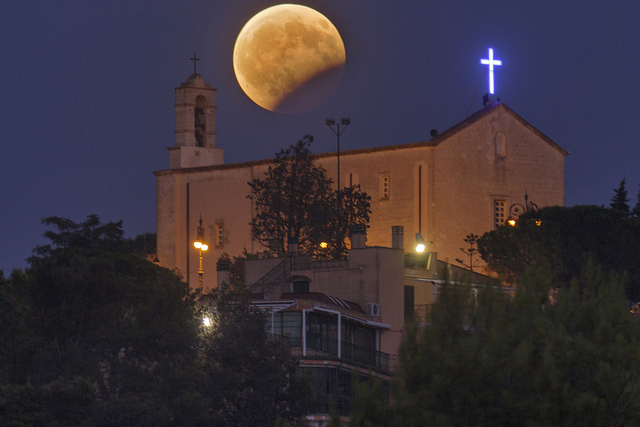
Partial Eclipse of Moon over the Church of Our Lady of the Bell in Casarano, Sicily, Italy. Single photo taken with a Konus 80/400 telescope and Canon 700d camera. Credit and copyright: Gianluca Belgrado.
Eclipsed full moon over the eastern horizon as seen from Treppendorf, Brandenburg, Germany. Credit and copyright: Andreas Schnabel.
Partial lunar eclipse of August 7th 2017, as seen from Bavaria, Germany at around 19:17 UTC. Shot with an EOS 550D mounted to a Meade ETX 70 Telescope. Exposure was 1/125 seconds with ISO 100. Credit and copyright:
Stephan Haverland.
The partial lunar eclipse as see from Czolpino, Pomerania, Poland. Credit and copyright:
Pawel Warchal.
A view of the partial lunar eclipse on August 7, 2017 as seen from Malta in the Mediterranean Sea. Credit and copyright: Leonard Ellul-Mercer.Here is a video of additional images from Leonard Mercer:
You can watch a reply of a live webcast from the Virtual Telescope Project of the partial lunar eclipse seen from Rome:
The post Gorgeous Images of the August 2017 Partial Lunar Eclipse appeared first on Universe Today.
Just to get you in the mood for the upcoming total solar eclipse — now less than two weeks away — our Solar System put on a little eclipse display of the lunar kind on August 7. The full Moon passed through part of the Earth’s umbral shadow, and the timing made this partial lunar eclipse visible in parts of Europe and Africa.
Thanks to our friends around the world who posted in Universe Today’s Flickr page, we’ve got images to share! Enjoy the views! Click on all the images to see larger versions of them on Flickr. The lead image link is here.
And for those of you in the path of the August 21 solar eclipse, please feel free to share your images on our Flickr page, and we may feature them in an upcoming article.
A composite of images take during the August 2017 lunar eclipse, as see from Kuala Lumpur. Credit and copyright: Shahrin Ahmad.
Partial lunar eclipse seen from Lausanne’s lakeshore in Switzerland … The Moon had just moved up from behind the Tour d’Aï Peaks. Credit and copyright: Hicham Dennaoui.
Partial Eclipse of Moon over the Church of Our Lady of the Bell in Casarano, Sicily, Italy. Single photo taken with a Konus 80/400 telescope and Canon 700d camera. Credit and copyright: Gianluca Belgrado.
Eclipsed full moon over the eastern horizon as seen from Treppendorf, Brandenburg, Germany. Credit and copyright: Andreas Schnabel.
Partial lunar eclipse of August 7th 2017, as seen from Bavaria, Germany at around 19:17 UTC. Shot with an EOS 550D mounted to a Meade ETX 70 Telescope. Exposure was 1/125 seconds with ISO 100. Credit and copyright:
Stephan Haverland.
The partial lunar eclipse as see from Czolpino, Pomerania, Poland. Credit and copyright:
Pawel Warchal.
A view of the partial lunar eclipse on August 7, 2017 as seen from Malta in the Mediterranean Sea. Credit and copyright: Leonard Ellul-Mercer.
You can watch a reply of a live webcast from the Virtual Telescope Project of the partial lunar eclipse seen from Rome:
The post Gorgeous Images of the August 2017 Partial Lunar Eclipse appeared first on Universe Today.
New Horizons’ Next Flyby Target Just Got Weirder!
New Horizons’ Next Flyby Target Just Got Weirder!:
Since it made its historic flyby of Pluto in July of 2015, the New Horizons mission has been venturing farther into the outer Solar System. With the spacecraft still healthy and its system in working order, the mission was extended to include the exploration of additional Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs). The first target for this part of its mission is the KBO known as 2014 MU69, which New Horizons is currently making its way towards.
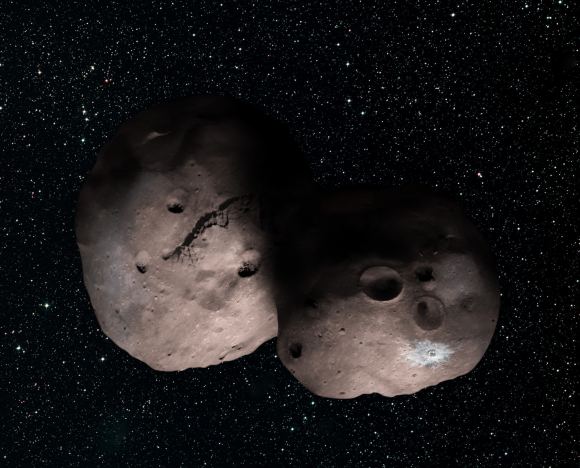
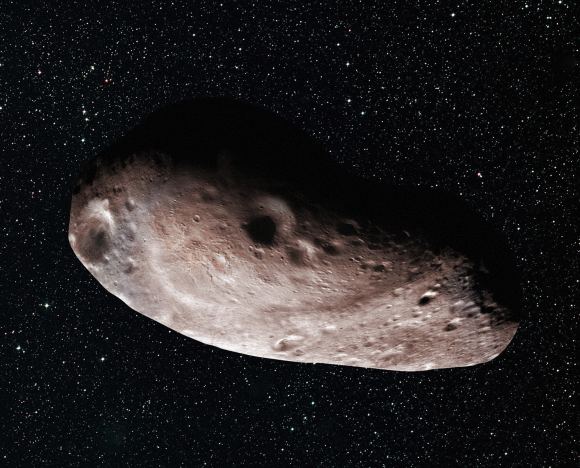
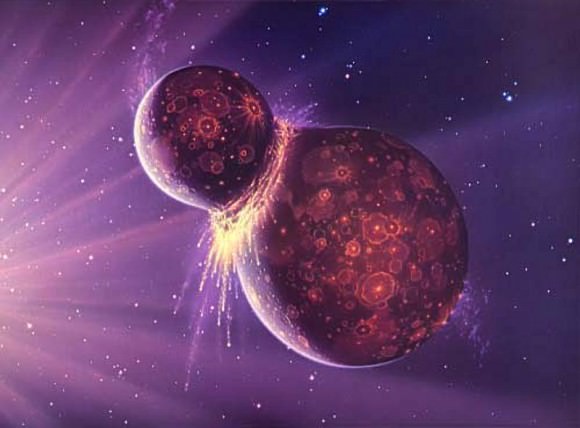
In the past, NASA believed this object was a spherical chunk of ice and rock measuring 18–41 km (10–30 mi) in diameter. However, a more recent occultation observation has led the New Horizon‘s team to conclude that MU69 may actually be a large object with a chunk taken out of it (an “extreme prolate spheroid”) or two objects orbiting very closely together or touching – aka. a close or contact binary.
In 2015, MU69 was identified as one of two potential destinations for New Horizons and was recommended to NASA by the mission science team. It was selected because of the immense opportunities for research it presented. As Alan Stern, the Principle Investigator (PI) for the New Horizons mission at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), indicated at the time:
Artist’s concept of a binary object, which new data suggests 2014 MU69 (the next flyby target for NASA’s New Horizons mission) could be. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI/Alex ParkerThe most recent observation of the KBO took place on July 17th, 2017, when the object passed in front of a star. This provided the New Horizon’s team with an opportunity to measure the resulting dip in the star’s luminosity – aka. an occultation – using a series of telescopes that they had deployed to a remote part of Patagonia, Argentina. These sorts of observations are performed regularly in order to obtain estimates of an asteroid’s size and position.
In the case of MU69’s occulation, the New Horizons team was able to obtain vital data that will help the mission planners to plot the trajectory of their flyby. In addition, the data revealed things about MU69’s size, shape, orbit, and the environment that surrounds it. It was because of this that the team began to question earlier estimates on the object’s size and shape.
Based on their new observations, they are confident that the object is no more than 30 km (20 mi) long, if it is an extreme prolate spheroid. If, however, it is a binary, the two objects that compose it are believed to measure about 15-20 km (9-12 mi) in diameter each. Alan Stern expanded on these new findings in a recent NASA press statement, saying:
Artist’s concept of Kuiper Belt object 2014 MU69 as a single body (above) with a large chunk taken out of it. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI/Alex ParkerThe recent stellar occulation was the third of three observations conducted for the New Horizons mission. To prepare for the event, the New Horizons team traveled to Argentina and South Africa on June 3rd. On July 10th, a week before the occultation, NASA’s airborne Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) provided support by studying the space around MU69.
Using its 2.5 m (100-inch) telescope, SOFIA was looking for debris that might present a hazard to New Horizons spacecraft as it makes its flyby less than 17 months from now. Last, but certainly not least, the team also relied on data provided by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the ESA’s Gaia satellite to calculate and pinpoint where MU69 would cast its shadow on Earth’s surface.
Thanks to their assistance, the New Horizons team knew exactly where the occultation shadow would be and set up their “fence line” of small, mobile telescopes accordingly. Marc Buie – the New Horizons co-investigator – was responsible for leading the observation campaign. As he explained, the data it yielded will be of great help in the planning the flyby, but also indicated that their could be some surprises in the future:
“These exciting and puzzling results have already been key for our mission planning,” he said, “but also add to the mysteries surrounding this target leading into the New Horizons encounter with MU69, now less than 17 months away.”
The flyby with MU69 is scheduled to take place on Jan. 1st, 2019, and will be the most distant flyby in the history of space exploration. In addition to being 1.6 billion km (1 billion mi) from Pluto, the New Horizons spacecraft will be 6.5 billion km (4 billion mi) from Earth! What’s more, the first-ever study of a KBO is expected to yield some fantastic scientific data, and tell us much about the formation and evolution of our Solar System.
Further Reading: NASA
The post New Horizons’ Next Flyby Target Just Got Weirder! appeared first on Universe Today.
Since it made its historic flyby of Pluto in July of 2015, the New Horizons mission has been venturing farther into the outer Solar System. With the spacecraft still healthy and its system in working order, the mission was extended to include the exploration of additional Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs). The first target for this part of its mission is the KBO known as 2014 MU69, which New Horizons is currently making its way towards.
In the past, NASA believed this object was a spherical chunk of ice and rock measuring 18–41 km (10–30 mi) in diameter. However, a more recent occultation observation has led the New Horizon‘s team to conclude that MU69 may actually be a large object with a chunk taken out of it (an “extreme prolate spheroid”) or two objects orbiting very closely together or touching – aka. a close or contact binary.
In 2015, MU69 was identified as one of two potential destinations for New Horizons and was recommended to NASA by the mission science team. It was selected because of the immense opportunities for research it presented. As Alan Stern, the Principle Investigator (PI) for the New Horizons mission at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), indicated at the time:
“2014 MU69 is a great choice because it is just the kind of ancient KBO, formed where it orbits now, that the Decadal Survey desired us to fly by. Moreover, this KBO costs less fuel to reach [than other candidate targets], leaving more fuel for the flyby, for ancillary science, and greater fuel reserves to protect against the unforeseen.”
Artist’s concept of a binary object, which new data suggests 2014 MU69 (the next flyby target for NASA’s New Horizons mission) could be. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI/Alex Parker
In the case of MU69’s occulation, the New Horizons team was able to obtain vital data that will help the mission planners to plot the trajectory of their flyby. In addition, the data revealed things about MU69’s size, shape, orbit, and the environment that surrounds it. It was because of this that the team began to question earlier estimates on the object’s size and shape.
Based on their new observations, they are confident that the object is no more than 30 km (20 mi) long, if it is an extreme prolate spheroid. If, however, it is a binary, the two objects that compose it are believed to measure about 15-20 km (9-12 mi) in diameter each. Alan Stern expanded on these new findings in a recent NASA press statement, saying:
“This new finding is simply spectacular. The shape of MU69 is truly provocative, and could mean another first for New Horizons going to a binary object in the Kuiper Belt. I could not be happier with the occultation results, which promise a scientific bonanza for the flyby.”
Artist’s concept of Kuiper Belt object 2014 MU69 as a single body (above) with a large chunk taken out of it. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI/Alex Parker
Using its 2.5 m (100-inch) telescope, SOFIA was looking for debris that might present a hazard to New Horizons spacecraft as it makes its flyby less than 17 months from now. Last, but certainly not least, the team also relied on data provided by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the ESA’s Gaia satellite to calculate and pinpoint where MU69 would cast its shadow on Earth’s surface.
Thanks to their assistance, the New Horizons team knew exactly where the occultation shadow would be and set up their “fence line” of small, mobile telescopes accordingly. Marc Buie – the New Horizons co-investigator – was responsible for leading the observation campaign. As he explained, the data it yielded will be of great help in the planning the flyby, but also indicated that their could be some surprises in the future:
“These exciting and puzzling results have already been key for our mission planning,” he said, “but also add to the mysteries surrounding this target leading into the New Horizons encounter with MU69, now less than 17 months away.”
The flyby with MU69 is scheduled to take place on Jan. 1st, 2019, and will be the most distant flyby in the history of space exploration. In addition to being 1.6 billion km (1 billion mi) from Pluto, the New Horizons spacecraft will be 6.5 billion km (4 billion mi) from Earth! What’s more, the first-ever study of a KBO is expected to yield some fantastic scientific data, and tell us much about the formation and evolution of our Solar System.
Further Reading: NASA
The post New Horizons’ Next Flyby Target Just Got Weirder! appeared first on Universe Today.
What are Gas Giants?
What are Gas Giants?:
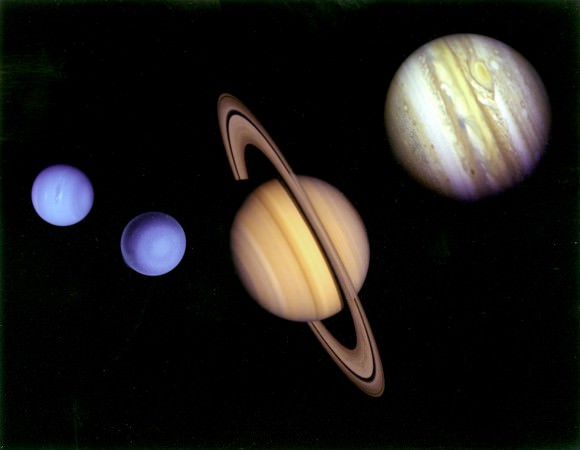
Between the planets of the inner and outer Solar System, there are some stark differences. The planets that resides closer to the Sun are terrestrial (i.e. rocky) in nature, meaning that they are composed of silicate minerals and metals. Beyond the Asteroid Belt, however, the planets are predominantly composed of gases, and are much larger than their terrestrial peers.
This is why astronomers use the term “gas giants” when referring to the planets of the outer Solar System. The more we’ve come to know about these four planets, the more we’ve come to understand that no two gas giants are exactly alike. In addition, ongoing studies of planets beyond our Solar System (aka. “extra-solar planets“) has shown that there are many types of gas giants that do not conform to Solar examples. So what exactly is a “gas giant”?
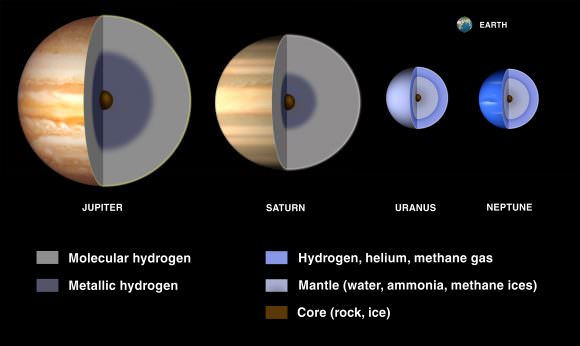
The four gas giants of the Solar System (from right to left): Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Credit: NASA/JPLWhat’s more, gas giants are also thought to have large concentrations of metal and silicate material in their cores. Nevertheless, the term has remained in popular usage for decades and refers to all planets – be they Solar or extra-solar in nature – that are composed mainly of gases. It is also in keeping with the practice of planetary scientists, who use a shorthand – i.e. “rock”, “gas”, and “ice” – to classify planets based on the most common element within them.
Hence the difference between Jupiter and Saturn on the one and, and Uranus and Neptune on the other. Due to the high concentrations of volatiles (such as water, methane and ammonia) within the latter two – which planetary scientists classify as “ices” – these two giant planets are often called “ice giants”. But since they are composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, they are still considered gas giants alongside Jupiter and Saturn.
Class I: Ammonia Clouds – this class applies to gas giants whose appearances are dominated by ammonia clouds, and which are found in the outer regions of a planetary system. In other words, it applies only to planets that are beyond the “Frost Line”, the distance in a solar nebula from the central protostar where volatile compounds – i.e. water, ammonia, methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide – condense into solid ice grains.
These cutaways illustrate interior models of the giant planets. Jupiter is shown with a rocky core overlaid by a deep layer of metallic hydrogen. Credit: NASA/JPLClass II: Water Clouds – this applies to planets that have average temperatures typically below 250 K (-23 °C; -9 °F), and are therefore too warm to form ammonia clouds. Instead, these gas giants have clouds that are formed from condensed water vapor. Since water is more reflective than ammonia, Class II gas giants have higher albedos.
Class III: Cloudless – this class applies to gas giants that are generally warmer – 350 K (80 °C; 170 °F) to 800 K ( 530 °C; 980 °F) – and do not form cloud cover because they lack the necessary chemicals. These planets have low albedos since they do not reflect as much light into space. These bodies would also appear like clear blue globes because of the way methane in their atmospheres absorbs light (like Uranus and Neptune).
Class IV: Alkali Metals – this class of planets experience temperatures in excess of 900 K (627 °C; 1160 °F), at which point Carbon Monoxide becomes the dominant carbon-carrying molecule in their atmospheres (rather than methane). The abundance of alkali metals also increases substantially, and cloud decks of silicates and metals form deep in their atmospheres. Planets belonging to Class IV and V are referred to as “Hot Jupiters”.
Class V: Silicate Clouds – this applies to the hottest of gas giants, with temperatures above 1400 K (1100 °C; 2100 °F), or cooler planets with lower gravity than Jupiter. For these gas giants, the silicate and iron cloud decks are believed to be high up in the atmosphere. In the case of the former, such gas giants are likely to glow red from thermal radiation and reflected light.
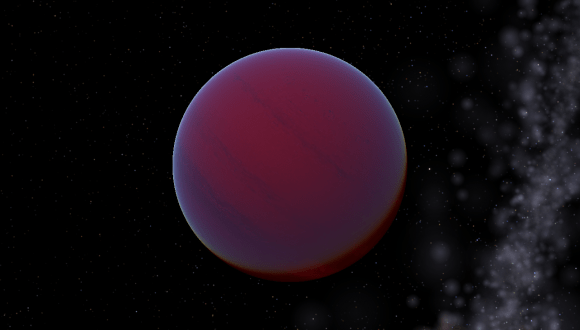
Artist’s concept of “hot Jupiter” exoplanet, a gas giant that orbits very close to its star. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
As such, exoplanet-hunters tend to designate extra-solar gas giants based on their apparent sizes and distances from their stars. In the case of the former, they are often referred to as “Super-Jupiters”, Jupiter-sized, and Neptune-sized. To date, these types of exoplanet account for the majority of discoveries made by Kepler and other missions, since their larger sizes and greater distances from their stars makes them the easiest to detect.
In terms of their respective distances from their sun, exoplanet-hunters divide extra-solar gas giants into two categories: “cold gas giants” and “hot Jupiters”. Typically, cold hydrogen-rich gas giants are more massive than Jupiter but less than about 1.6 Jupiter masses, and will only be slightly larger in volume than Jupiter. For masses above this, gravity will cause the planets to shrink.
Exoplanet surveys have also turned up a class of planet known as “gas dwarfs”, which applies to hydrogen planets that are not as large as the gas giants of the Solar System. These stars have been observed to orbit close to their respective stars, causing them to lose atmospheric mass faster than planets that orbit at greater distances.
For gas giants that occupy the mass range between 13 to 75-80 Jupiter masses, the term “brown dwarf” is used. This designation is reserved for the largest of planetary/substellar objects; in other words, objects that are incredibly large, but not quite massive enough to undergo nuclear fusion in their core and become a star. Below this range are sub-brown dwarfs, while anything above are known as the lightest red dwarf (M9 V) stars.
Like all things astronomical in nature, gas giants are diverse, complex, and immensely fascinating. Between missions that seek to examine the gas giants of our Solar System directly to increasingly sophisticated surveys of distant planets, our knowledge of these mysterious objects continues to grow. And with that, so is our understanding of how star systems form and evolve.
We have written many interesting articles about gas giants here at Universe Today. Here’s The Planet Jupiter, The Planet Saturn, The Planet Uranus, The Planet Neptune, What are the Jovian Planets?, What are the Outer Planets of the Solar System?, What’s Inside a Gas Giant?, and Which Planets Have Rings?
For more information, check out NASA’s Solar System Exploration.
Astronomy Cast also has some great episodes on the subject. Here’s Episode 56: Jupiter to get you started!
Sources:
Between the planets of the inner and outer Solar System, there are some stark differences. The planets that resides closer to the Sun are terrestrial (i.e. rocky) in nature, meaning that they are composed of silicate minerals and metals. Beyond the Asteroid Belt, however, the planets are predominantly composed of gases, and are much larger than their terrestrial peers.
This is why astronomers use the term “gas giants” when referring to the planets of the outer Solar System. The more we’ve come to know about these four planets, the more we’ve come to understand that no two gas giants are exactly alike. In addition, ongoing studies of planets beyond our Solar System (aka. “extra-solar planets“) has shown that there are many types of gas giants that do not conform to Solar examples. So what exactly is a “gas giant”?
Definition and Classification:
By definition, a gas giant is a planet that is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. The name was originally coined in 1952 by James Blish, a science fiction writer who used the term to refer to all giant planets. In truth, the term is something of a misnomer, since these elements largely take a liquid and solid form within a gas giant, as a result of the extreme pressure conditions that exist within the interior.The four gas giants of the Solar System (from right to left): Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Credit: NASA/JPL
Hence the difference between Jupiter and Saturn on the one and, and Uranus and Neptune on the other. Due to the high concentrations of volatiles (such as water, methane and ammonia) within the latter two – which planetary scientists classify as “ices” – these two giant planets are often called “ice giants”. But since they are composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, they are still considered gas giants alongside Jupiter and Saturn.
Classification:
Today, Gas giants are divided into five classes, based on the classification scheme proposed by David Sudarki (et al.) in a 2000 study. Titled “Albedo and Reflection Spectra of Extrasolar Giant Planets“, Sudarsky and his colleagues designated five different types of gas giant based on their appearances and albedo, and how this is affected by their respective distances from their star.Class I: Ammonia Clouds – this class applies to gas giants whose appearances are dominated by ammonia clouds, and which are found in the outer regions of a planetary system. In other words, it applies only to planets that are beyond the “Frost Line”, the distance in a solar nebula from the central protostar where volatile compounds – i.e. water, ammonia, methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide – condense into solid ice grains.
These cutaways illustrate interior models of the giant planets. Jupiter is shown with a rocky core overlaid by a deep layer of metallic hydrogen. Credit: NASA/JPL
Class III: Cloudless – this class applies to gas giants that are generally warmer – 350 K (80 °C; 170 °F) to 800 K ( 530 °C; 980 °F) – and do not form cloud cover because they lack the necessary chemicals. These planets have low albedos since they do not reflect as much light into space. These bodies would also appear like clear blue globes because of the way methane in their atmospheres absorbs light (like Uranus and Neptune).
Class IV: Alkali Metals – this class of planets experience temperatures in excess of 900 K (627 °C; 1160 °F), at which point Carbon Monoxide becomes the dominant carbon-carrying molecule in their atmospheres (rather than methane). The abundance of alkali metals also increases substantially, and cloud decks of silicates and metals form deep in their atmospheres. Planets belonging to Class IV and V are referred to as “Hot Jupiters”.
Class V: Silicate Clouds – this applies to the hottest of gas giants, with temperatures above 1400 K (1100 °C; 2100 °F), or cooler planets with lower gravity than Jupiter. For these gas giants, the silicate and iron cloud decks are believed to be high up in the atmosphere. In the case of the former, such gas giants are likely to glow red from thermal radiation and reflected light.
Artist’s concept of “hot Jupiter” exoplanet, a gas giant that orbits very close to its star. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Exoplanets:
The study of exoplanets has also revealed a wealth of other types of gas giants that are more massive than the Solar counterparts (aka. Super-Jupiters) as well as many that are comparable in size. Other discoveries have been a fraction of the size of their solar counterparts, while some have been so massive that they are just shy of becoming a star. However, given their distance from Earth, their spectra and albedo have cannot always be accurately measured.As such, exoplanet-hunters tend to designate extra-solar gas giants based on their apparent sizes and distances from their stars. In the case of the former, they are often referred to as “Super-Jupiters”, Jupiter-sized, and Neptune-sized. To date, these types of exoplanet account for the majority of discoveries made by Kepler and other missions, since their larger sizes and greater distances from their stars makes them the easiest to detect.
In terms of their respective distances from their sun, exoplanet-hunters divide extra-solar gas giants into two categories: “cold gas giants” and “hot Jupiters”. Typically, cold hydrogen-rich gas giants are more massive than Jupiter but less than about 1.6 Jupiter masses, and will only be slightly larger in volume than Jupiter. For masses above this, gravity will cause the planets to shrink.
Exoplanet surveys have also turned up a class of planet known as “gas dwarfs”, which applies to hydrogen planets that are not as large as the gas giants of the Solar System. These stars have been observed to orbit close to their respective stars, causing them to lose atmospheric mass faster than planets that orbit at greater distances.
For gas giants that occupy the mass range between 13 to 75-80 Jupiter masses, the term “brown dwarf” is used. This designation is reserved for the largest of planetary/substellar objects; in other words, objects that are incredibly large, but not quite massive enough to undergo nuclear fusion in their core and become a star. Below this range are sub-brown dwarfs, while anything above are known as the lightest red dwarf (M9 V) stars.
Like all things astronomical in nature, gas giants are diverse, complex, and immensely fascinating. Between missions that seek to examine the gas giants of our Solar System directly to increasingly sophisticated surveys of distant planets, our knowledge of these mysterious objects continues to grow. And with that, so is our understanding of how star systems form and evolve.
We have written many interesting articles about gas giants here at Universe Today. Here’s The Planet Jupiter, The Planet Saturn, The Planet Uranus, The Planet Neptune, What are the Jovian Planets?, What are the Outer Planets of the Solar System?, What’s Inside a Gas Giant?, and Which Planets Have Rings?
For more information, check out NASA’s Solar System Exploration.
Astronomy Cast also has some great episodes on the subject. Here’s Episode 56: Jupiter to get you started!
Sources:
- NASA – Solar System Exploration: Planets
- NASA – Gas Giant Interiors
- Space Facts – Gas Giants
- Wikipedia – Gas Giants
- The Planets – Gas Giants
New Study Claims There are Four Exoplanets Around Nearest Sun-Like Star!
New Study Claims There are Four Exoplanets Around Nearest Sun-Like Star!:
It has been an exciting time for the field of exoplanet studies lately! Last summer, researchers from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) announced the discovery of an Earth-like planet (Proxima b) located in the star system that is the nearest to our own. And just six months ago, an international team of astronomers announced the discovery of seven rocky planets orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1.
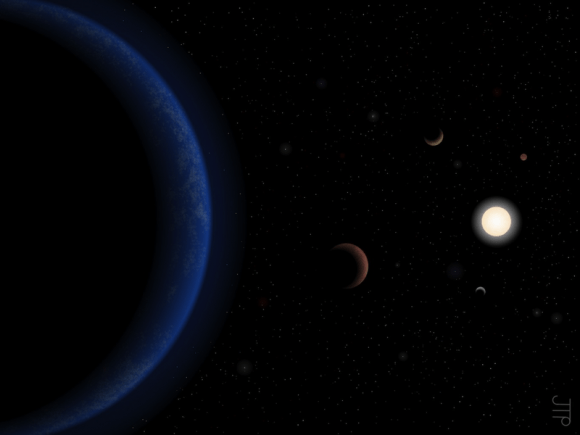
But in what could be the most encouraging discovery for those hoping to find a habitable planet beyond Earth, an an international team of astronomers just announced the discovery of four exoplanet candidates in the tau Ceti system. Aside from being close to the Solar System – just 12 light-years away – this find is also encouraging because the planet candidates orbit a star very much like our own!
The study that details these findings – “Color difference makes a difference: four planet candidates around tau Ceti” – recently appeared online and has been accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal. Led by researchers from the Center for Astrophysics Research (CAR) at the University of Hertfordshire, the team analyzed tau Ceti using a noise-eliminating model to determine the presence of four Earth-like planets.
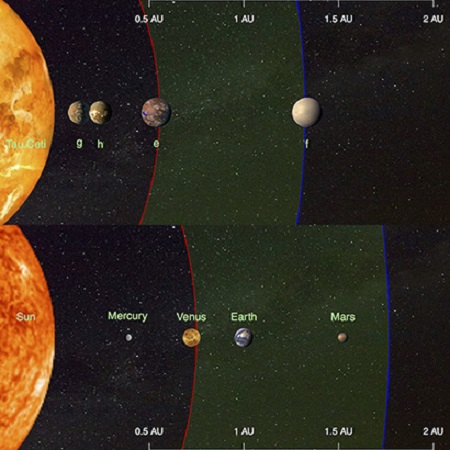
This illustration compares the four planets detected around the nearby star tau Ceti (top) and the inner planets of our solar system (bottom). Credit: Fabo Feng/CAR/Univ. of HertfordshireThis discovery was made possible thanks to ongoing improvements in instrumentation, observation and data-sharing, which are allowing for surveys of ever-increasing sensitivity. As Steven Vogt, a professor of astronomy and astrophysics at UC Santa Cruz and a co-author on the paper, said in a UCSC press release:
The team behind that study included several members who produced this latest study. At the time, lead author Mikko Tuomi (University of Hertfordshire, a co-author on the most recent one) was leading an effort to develop better data analysis techniques, and used this star as a benchmark case. As Tuomi explained, theses efforts allowed them to rule out two of the signals that has previously been identified as planets:
Artist’s impression of the Tau Ceti system, based on data retrieved in 2012. Credit: J. Pinfield/Univ. of HertfordshireFor the sake of this latest study – which was led by Fabo Feng, a member of the CAR – the team relied on data provided by the High Accuracy Radial velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS) spectrograph at the ESO’s La Silla Observatory in Chile, and the High Resolution Echelle Spectrometer (HIRES) instrument at the W. M. Keck Observatory in Mauna Kea, Hawaii.
From this, they were able to create a model that removed “wavelength dependent noise” from radial velocity measurements. After applying this model to surveys made of tau Ceti, they were able to obtain measurements that were sensitive enough to detect variations in the star’s movement as small as 30 cm per second. In the end, they concluded that tau Ceti has a system of no more than four exoplanets.
As Tuomi indicated, after several surveys and attempts to eliminate extraneous noise, astronomers may finally have a clear picture of how many planets tau Ceti has, and of what type. “[N]o matter how we look at the star, there seem to be at least four rocky planets orbiting it,” he said. “We are slowly learning to tell the difference between wobbles caused by planets and those caused by stellar active surface. This enabled us to essentially verify the existence of the two outer, potentially habitable planets in the system.”
They further estimate from their refined measurements that these planets have masses ranging from four Earth-masses (aka. “super-Earths”) to as low as 1.7 Earth masses, making them among the smallest planets ever detected around a nearby sun-like star. But most exciting of all is the fact that that two of these planets (tau Ceti e and f) are located within the star’s habitable zone.
Recent studies have shown that rocky planets orbiting red dwarf stars will be tidally-locked and subject to intense radiation, reducing their chances of being habitable. Credit: M. Weiss/CfAThe reason for this is because tau Ceti is a G-type (yellow dwarf) star, which makes it similar to our own Sun – about 0.78 times as massive and half as bright. In contrast, many recently discovered exoplanets – such as Proxima b and the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 – all orbit M-type (red dwarf) stars. Compared to our Sun, these stars are variable and unstable, increasing their chances of stripping the atmospheres of their respective planets.
In addition, since red dwarfs are much dimmer than our Sun, a rocky planet would have to orbit very closely to them in order to be within their habitable zones. At this kind of distance, the planet would likely be tidally-locked, meaning that one side would constantly be facing towards the sun. This too makes the odds of life emerging on any such planet pretty slim.
Because of this, astronomers have been looking forward to finding more exoplanets around stars that are closer in size, mass and luminosity to our own. But before anyone gets too excited, its important to note these worlds are Super-Earths – with up to four times the mass of Earth. This means that (depending on their density as well) any life that might emerge on these planets would be subject to significantly increased gravity.
In addition, a massive debris disc surrounds the star, which means that these outermost planets are probably subjected to intensive bombardment by asteroids and comets. This not doesn’t exactly bode well for potential life on these planets! Still, this study is very encouraging, and for a number of reasons. Beyond finding strong evidence of exoplanets around a Sun-like star, the measurements that led to their detection are the most sensitive to date.
At the rate that their methods are improving, researchers should be getting to the 10-centimeter-per-second limit in no time at all. This is the level of sensitively required for detecting Earth analogs – aka. the brass ring for exoplanet-hunters. As Feng indicated:
With an estimated 100 billion planets in our galaxy alone, we’re sure to find several Earths out here. One can only hope they have given rise to complex life like our own, and that they are in the mood to chat!
Further Reading: UCSC, arXiv
The post New Study Claims There are Four Exoplanets Around Nearest Sun-Like Star! appeared first on Universe Today.
It has been an exciting time for the field of exoplanet studies lately! Last summer, researchers from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) announced the discovery of an Earth-like planet (Proxima b) located in the star system that is the nearest to our own. And just six months ago, an international team of astronomers announced the discovery of seven rocky planets orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1.
But in what could be the most encouraging discovery for those hoping to find a habitable planet beyond Earth, an an international team of astronomers just announced the discovery of four exoplanet candidates in the tau Ceti system. Aside from being close to the Solar System – just 12 light-years away – this find is also encouraging because the planet candidates orbit a star very much like our own!
The study that details these findings – “Color difference makes a difference: four planet candidates around tau Ceti” – recently appeared online and has been accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal. Led by researchers from the Center for Astrophysics Research (CAR) at the University of Hertfordshire, the team analyzed tau Ceti using a noise-eliminating model to determine the presence of four Earth-like planets.
This illustration compares the four planets detected around the nearby star tau Ceti (top) and the inner planets of our solar system (bottom). Credit: Fabo Feng/CAR/Univ. of Hertfordshire
“We are now finally crossing a threshold where, through very sophisticated modeling of large combined data sets from multiple independent observers, we can disentangle the noise due to stellar surface activity from the very tiny signals generated by the gravitational tugs from Earth-sized orbiting planets.”This is the latest in a long-line of surveys of tau Ceti, which has been of interest to astronomers for decades. By 1988, several radial velocity measurements were conducted of the star system that ruled out the possibility of massive planets at Jupiter-like distances. In 2012, astronomers from UC Santa Barabara presented a study that indicated that tau Ceti might be orbited by five exoplanets, two of which were within the star’s habitable zone.
The team behind that study included several members who produced this latest study. At the time, lead author Mikko Tuomi (University of Hertfordshire, a co-author on the most recent one) was leading an effort to develop better data analysis techniques, and used this star as a benchmark case. As Tuomi explained, theses efforts allowed them to rule out two of the signals that has previously been identified as planets:
“We came up with an ingenious way of telling the difference between signals caused by planets and those caused by star’s activity. We realized that we could see how star’s activity differed at different wavelengths and use that information to separate this activity from signals of planets.”
Artist’s impression of the Tau Ceti system, based on data retrieved in 2012. Credit: J. Pinfield/Univ. of Hertfordshire
From this, they were able to create a model that removed “wavelength dependent noise” from radial velocity measurements. After applying this model to surveys made of tau Ceti, they were able to obtain measurements that were sensitive enough to detect variations in the star’s movement as small as 30 cm per second. In the end, they concluded that tau Ceti has a system of no more than four exoplanets.
As Tuomi indicated, after several surveys and attempts to eliminate extraneous noise, astronomers may finally have a clear picture of how many planets tau Ceti has, and of what type. “[N]o matter how we look at the star, there seem to be at least four rocky planets orbiting it,” he said. “We are slowly learning to tell the difference between wobbles caused by planets and those caused by stellar active surface. This enabled us to essentially verify the existence of the two outer, potentially habitable planets in the system.”
They further estimate from their refined measurements that these planets have masses ranging from four Earth-masses (aka. “super-Earths”) to as low as 1.7 Earth masses, making them among the smallest planets ever detected around a nearby sun-like star. But most exciting of all is the fact that that two of these planets (tau Ceti e and f) are located within the star’s habitable zone.
Recent studies have shown that rocky planets orbiting red dwarf stars will be tidally-locked and subject to intense radiation, reducing their chances of being habitable. Credit: M. Weiss/CfA
In addition, since red dwarfs are much dimmer than our Sun, a rocky planet would have to orbit very closely to them in order to be within their habitable zones. At this kind of distance, the planet would likely be tidally-locked, meaning that one side would constantly be facing towards the sun. This too makes the odds of life emerging on any such planet pretty slim.
Because of this, astronomers have been looking forward to finding more exoplanets around stars that are closer in size, mass and luminosity to our own. But before anyone gets too excited, its important to note these worlds are Super-Earths – with up to four times the mass of Earth. This means that (depending on their density as well) any life that might emerge on these planets would be subject to significantly increased gravity.
In addition, a massive debris disc surrounds the star, which means that these outermost planets are probably subjected to intensive bombardment by asteroids and comets. This not doesn’t exactly bode well for potential life on these planets! Still, this study is very encouraging, and for a number of reasons. Beyond finding strong evidence of exoplanets around a Sun-like star, the measurements that led to their detection are the most sensitive to date.
At the rate that their methods are improving, researchers should be getting to the 10-centimeter-per-second limit in no time at all. This is the level of sensitively required for detecting Earth analogs – aka. the brass ring for exoplanet-hunters. As Feng indicated:
“Our detection of such weak wobbles is a milestone in the search for Earth analogs and the understanding of the Earth’s habitability through comparison with these analogs. We have introduced new methods to remove the noise in the data in order to reveal the weak planetary signals.”Think of it! In no time at all, exoplanet-hunters could be finding a plethora of planets that are not only very close in size and mass to Earth, but also orbiting within their stars habitable zones. At that point, scientists are sure to dispense with decidedly vague terms like “potentially habitable” and “Earth-like” and begin using terms like “Earth-analog” confidently. No more ambiguity, just the firm conviction that Earth is not unique!
With an estimated 100 billion planets in our galaxy alone, we’re sure to find several Earths out here. One can only hope they have given rise to complex life like our own, and that they are in the mood to chat!
Further Reading: UCSC, arXiv
The post New Study Claims There are Four Exoplanets Around Nearest Sun-Like Star! appeared first on Universe Today.
New Study Says Moon’s Magnetic Field Existed 1 Billion Years Longer Than We Thought
New Study Says Moon’s Magnetic Field Existed 1 Billion Years Longer Than We Thought:
When it comes to the study of planets, moons, and stars, magnetic fields are kind of a big deal. Believed to be the result of convection in a planet, these fields can be the difference between a planet giving rise to life or becoming a lifeless ball of rock. For some time, scientists have known that has a Earth’s magnetic field, which is powered by a dynamo effect created by convection in its liquid, outer core.
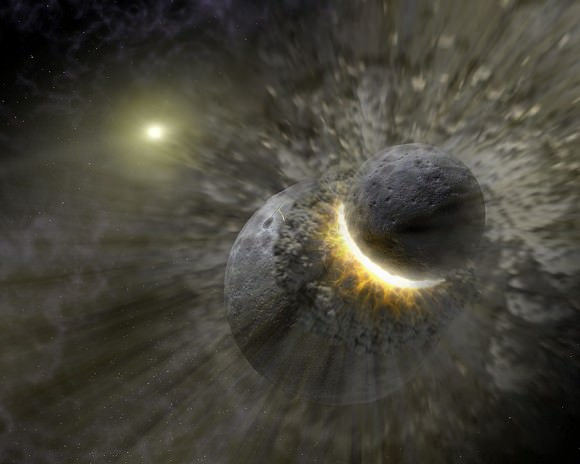
Scientists have also long held that the Moon once had a magnetic field, which was also powered by convection in its core. Previously, it was believed that this field disappeared roughly 1 billion years after the Moon formed (ca. 3 to 3.5 billion years ago). But according to a new study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), it now appears that the Moon’s magnetic field continued to exist for another billion years.
The study, titled “A two-billion-year history for the lunar dynamo“, recently appeared in the journal Science Advances. Led by Dr. Sonia Tikoo, an Assistant Professor at Rutger’s University and a former researcher at MIT, the team analyzed ancient lunar rocks collected by NASA’s Apollo 15 mission. What they found was that the rock showed signs of a being in magnetic field when it was formed between 1 and 2.5 billion years ago.
Artist’s concept of a collision between proto-Earth and Theia, which led to the formation of Moon, ca. 4.5 billion years ago. Credit: NASAThe age of this rock sample means that it is significantly younger than others returned by the Apollo missions. Using a technique they developed, the team examined the sample’s glassy composition with a magnometer to determine its magnetic properties. They then exposed the sample to a lab-generated magnetic field and other conditions that were similar to those that existed on the Moon when the rock would have formed.
This was done by placing the rocks into a specially-designed oxygen-deprived oven, which was built with the help of Clement Suavet and Timothy Grove – two researchers from MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS) and co-authors on the study. The team then exposed the rocks to a tenuous, oxygen-free environment and heated them to extreme temperatures.
As Benjamin Weiss – a professor of planetary sciences at EAPS – explained:
Previously, scientists suspected that the Moon’s magnetic field died out 1.5 billion years after the Moon formed (ca. 3 billion years ago). However, they were unsure if this process happened rapidly, or if the Moon’s magnetic field endured, but in a weakened state. The results of this study indicate that the magnetic field did in fact linger for an additional billion years, dissipating about 2.5 billion years ago.
As Weiss indicated, this study raises new questions about the Moon’s geological history:
In the past, scientists have proposed that the Moon’s dynamo was powered by Earth’s gravitational pull, which would have caused tidal flexing in the Moon’s interior (much in the same way that Jupiter and Saturn’s powerful gravity drives geological activity in their moons interiors). In addition, the Moon once orbited much closer to Earth, which may have been enough to power its once-stronger magnetic field.
Artist’s impression of a Mars-sized object crashing into the Earth, starting the process that eventually created our Moon. Credit: Joe TucciaroneHowever, the Moon gradually moved away from Earth, eventually reaching its current orbit about 3 billion years ago. This coincides with the timeline of the Moon’s magnetic field, which began to dissipate at about the same time. This could mean that by about 3 billion years ago, without the gravitational pull of the Earth, the core slowly cooled. One billion years later, the core had solidified to the point that it arrested the Moon;s magnetic field. As Weiss explained:
The results of these and other studies that seek to understand how the Moon formed and changed over time will also go a long way towards improving our understanding of how Earth, the Solar System, and extra-solar systems came to be.
Further Reading: Science Advances, MIT News
The post New Study Says Moon’s Magnetic Field Existed 1 Billion Years Longer Than We Thought appeared first on Universe Today.
When it comes to the study of planets, moons, and stars, magnetic fields are kind of a big deal. Believed to be the result of convection in a planet, these fields can be the difference between a planet giving rise to life or becoming a lifeless ball of rock. For some time, scientists have known that has a Earth’s magnetic field, which is powered by a dynamo effect created by convection in its liquid, outer core.
Scientists have also long held that the Moon once had a magnetic field, which was also powered by convection in its core. Previously, it was believed that this field disappeared roughly 1 billion years after the Moon formed (ca. 3 to 3.5 billion years ago). But according to a new study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), it now appears that the Moon’s magnetic field continued to exist for another billion years.
The study, titled “A two-billion-year history for the lunar dynamo“, recently appeared in the journal Science Advances. Led by Dr. Sonia Tikoo, an Assistant Professor at Rutger’s University and a former researcher at MIT, the team analyzed ancient lunar rocks collected by NASA’s Apollo 15 mission. What they found was that the rock showed signs of a being in magnetic field when it was formed between 1 and 2.5 billion years ago.
Artist’s concept of a collision between proto-Earth and Theia, which led to the formation of Moon, ca. 4.5 billion years ago. Credit: NASA
This was done by placing the rocks into a specially-designed oxygen-deprived oven, which was built with the help of Clement Suavet and Timothy Grove – two researchers from MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS) and co-authors on the study. The team then exposed the rocks to a tenuous, oxygen-free environment and heated them to extreme temperatures.
As Benjamin Weiss – a professor of planetary sciences at EAPS – explained:
“You see how magnetized it gets from getting heated in that known magnetic field, then you compare that field to the natural magnetic field you measured beforehand, and from that you can figure out what the ancient field strength was… In this way, we finally have gotten an accurate measurement of the lunar field.”From this, they determined the lunar rock became magnetized in a field with a strength of about 5 microtesla. That’s many times weaker than Earth’s magnetic field when measured from the surface (25 – 65 microteslas), and two orders of magnitude weaker than what it was 3 to 4 billion years ago. These findings were quite significant, since they may help to resolve an enduring mystery about the Moon.
Previously, scientists suspected that the Moon’s magnetic field died out 1.5 billion years after the Moon formed (ca. 3 billion years ago). However, they were unsure if this process happened rapidly, or if the Moon’s magnetic field endured, but in a weakened state. The results of this study indicate that the magnetic field did in fact linger for an additional billion years, dissipating about 2.5 billion years ago.
As Weiss indicated, this study raises new questions about the Moon’s geological history:
“The concept of a planetary magnetic field produced by moving liquid metal is an idea that is really only a few decades old. What powers this motion on Earth and other bodies, particularly on the moon, is not well-understood. We can figure this out by knowing the lifetime of the lunar dynamo.”In other words, this new timeline of the Moon casts some doubt on the theory that a lunar dynamo alone is what powered its magnetic field in the past. Basically, it is now seen as a distinct possibility that the Moon’s magnetic field was powered by two mechanisms. Whereas one allowed for a dynamo in the core that powered its magnetic field for a good billion years after the Moon’s formation, a second one kept it going afterwards.
In the past, scientists have proposed that the Moon’s dynamo was powered by Earth’s gravitational pull, which would have caused tidal flexing in the Moon’s interior (much in the same way that Jupiter and Saturn’s powerful gravity drives geological activity in their moons interiors). In addition, the Moon once orbited much closer to Earth, which may have been enough to power its once-stronger magnetic field.
Artist’s impression of a Mars-sized object crashing into the Earth, starting the process that eventually created our Moon. Credit: Joe Tucciarone
“As the moon cools, its core acts like a lava lamp – low-density stuff rises because it’s hot or because its composition is different from that of the surrounding fluid. That’s how we think the Earth’s dynamo works, and that’s what we suggest the late lunar dynamo was doing as well… Today the moon’s field is essentially zero. And we now know it turned off somewhere between the formation of this rock and today.”These findings were made possible thanks in part by the availability of younger lunar rocks. In the future, the researchers are planning on analyzing even younger samples to precisely determine where the Moon’s dynamo died out completely. This will not only serve to validate the findings of this study, but could also lead to a more comprehensive timeline of the Moon’s geological history.
The results of these and other studies that seek to understand how the Moon formed and changed over time will also go a long way towards improving our understanding of how Earth, the Solar System, and extra-solar systems came to be.
Further Reading: Science Advances, MIT News
The post New Study Says Moon’s Magnetic Field Existed 1 Billion Years Longer Than We Thought appeared first on Universe Today.
Star Ark: A Living, Self-Sustaining Spaceship
Star Ark: A Living, Self-Sustaining Spaceship:
Think of the ease. With a simple command of “Make it so” humans travelled from one star to the next in less time than for drinking a cup of coffee. At least that’s what happens in the time-restricted domain of television. In reality it’s not so easy. Nor does Rachel Armstrong misrepresent this point in her book of essays within “Star Ark – A Living Self-Sustaining Spaceship“; a book that brings some fundamental reality to star travel.
Yes, many people want to travel to other stars. We’re not ready for that. We’re still just planning on getting outside Earth’s protective atmosphere (again). Yet making preparations and doing judicious planning is the aim of this book. Wisely though, this book isn’t technical. It has no mention of specific impulse calculations or ion shields. Rather, this book takes a very liberal view of space travel and ponders deep questions such as whether the cosmos is an ecosystem.
Does our species have an appropriate culture for space travel? What exactly is a human? These concerns get raised in some very thought provoking sections. And given that the editor is an architect and one who apparently considers the emotional qualities of a structure as much as functional qualities, then this book’s presentation tends to be a little more on the philosophical side of things.
In particular, it looks at the benefits of living entities. For instance it notes that humans live in symbiotic relationships with a host of internal and external organisms. Most have already gone into space either within people who have traveled in space or possibly upon probes sent to other planets. So we aren’t the only species that’s traveled beyond Earth. But which beings are sufficient and necessary to keep humans alive for the generations needed to travel to another star? That question and many answers come up often.
As well, the essays get into bigger questions such as: What is life? Could the vessel be an organic construct? How might today’s humans evolve to tomorrow’s star travelers? Should humans travel in space and promote/continue panspermia? Yes, these questions and many more are raised in the essays collected within this book. And true to form for any book considering star travel, there aren’t any strict answers. There are however lots of ideas and concepts to better prepare humans.
Much of this book seems to center around the authors’ involvement with the Persephone project of Icarus Interstellar. Yet there’s very little description of either. However, the book does have wonderful descriptions of Biitschli experiments, explanations of living walls and critiques of theatrical productions.
There are a few fictional passages and some poetry. The long list of references indicates a broad knowledge of the technical issues, though the focus is on humanity and the living aspect. This focus flows through the essays, but having a collection of many authors makes for a disjointed flow. The writing styles are unique, the viewpoints are particular and the emphasis specialized for each. One common viewpoint does keep arising though. That is, we are already on a living spaceship; the Earth. Earth gives a unique platform for assessing the ability to travel to other stars. The essays state that it is or at least was a veritable, closed self-sustaining life support system. And, as seems to be the norm these days, the essays acknowledge that solutions for space travel would be just as good for people remaining behind upon Earth or travelling to the Moon or to Mars and so on. This care and concern for living organism keeps the book grounded, so to speak.
The all-encompassing-solution-finder may be a strength or a weakness to Rachel Armstrong’s collection within the book “Star Ark – A Living Self-Sustaining Spaceship”. As the book’s essays describe, humans have an incredible ability to think and act in abstract fashion. Just envisioning an attempt to send sentient beings to another star demonstrates this. But will we be able to enact this idea and what form might a star vessel take? Reading of this is easy. Will taking the necessary steps be just as easy?
The book is available here through Springer.
Learn more about the author, Rachel Armstrong, here.
The post Star Ark: A Living, Self-Sustaining Spaceship appeared first on Universe Today.
Think of the ease. With a simple command of “Make it so” humans travelled from one star to the next in less time than for drinking a cup of coffee. At least that’s what happens in the time-restricted domain of television. In reality it’s not so easy. Nor does Rachel Armstrong misrepresent this point in her book of essays within “Star Ark – A Living Self-Sustaining Spaceship“; a book that brings some fundamental reality to star travel.
Yes, many people want to travel to other stars. We’re not ready for that. We’re still just planning on getting outside Earth’s protective atmosphere (again). Yet making preparations and doing judicious planning is the aim of this book. Wisely though, this book isn’t technical. It has no mention of specific impulse calculations or ion shields. Rather, this book takes a very liberal view of space travel and ponders deep questions such as whether the cosmos is an ecosystem.
Does our species have an appropriate culture for space travel? What exactly is a human? These concerns get raised in some very thought provoking sections. And given that the editor is an architect and one who apparently considers the emotional qualities of a structure as much as functional qualities, then this book’s presentation tends to be a little more on the philosophical side of things.
In particular, it looks at the benefits of living entities. For instance it notes that humans live in symbiotic relationships with a host of internal and external organisms. Most have already gone into space either within people who have traveled in space or possibly upon probes sent to other planets. So we aren’t the only species that’s traveled beyond Earth. But which beings are sufficient and necessary to keep humans alive for the generations needed to travel to another star? That question and many answers come up often.
As well, the essays get into bigger questions such as: What is life? Could the vessel be an organic construct? How might today’s humans evolve to tomorrow’s star travelers? Should humans travel in space and promote/continue panspermia? Yes, these questions and many more are raised in the essays collected within this book. And true to form for any book considering star travel, there aren’t any strict answers. There are however lots of ideas and concepts to better prepare humans.
Much of this book seems to center around the authors’ involvement with the Persephone project of Icarus Interstellar. Yet there’s very little description of either. However, the book does have wonderful descriptions of Biitschli experiments, explanations of living walls and critiques of theatrical productions.
There are a few fictional passages and some poetry. The long list of references indicates a broad knowledge of the technical issues, though the focus is on humanity and the living aspect. This focus flows through the essays, but having a collection of many authors makes for a disjointed flow. The writing styles are unique, the viewpoints are particular and the emphasis specialized for each. One common viewpoint does keep arising though. That is, we are already on a living spaceship; the Earth. Earth gives a unique platform for assessing the ability to travel to other stars. The essays state that it is or at least was a veritable, closed self-sustaining life support system. And, as seems to be the norm these days, the essays acknowledge that solutions for space travel would be just as good for people remaining behind upon Earth or travelling to the Moon or to Mars and so on. This care and concern for living organism keeps the book grounded, so to speak.
The all-encompassing-solution-finder may be a strength or a weakness to Rachel Armstrong’s collection within the book “Star Ark – A Living Self-Sustaining Spaceship”. As the book’s essays describe, humans have an incredible ability to think and act in abstract fashion. Just envisioning an attempt to send sentient beings to another star demonstrates this. But will we be able to enact this idea and what form might a star vessel take? Reading of this is easy. Will taking the necessary steps be just as easy?
The book is available here through Springer.
Learn more about the author, Rachel Armstrong, here.
The post Star Ark: A Living, Self-Sustaining Spaceship appeared first on Universe Today.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)